 | |
WPW case 2. (With LAD and pseudo infarct Q wave) | |
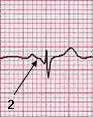
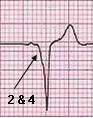
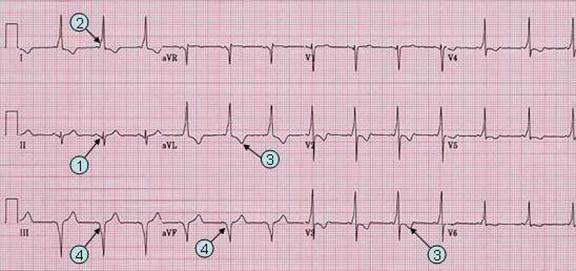
| Note that PR interval (1) in lead II is also short. The QRS begin with broad and shallow Q wave, which is a delta wave. | |
| Patient. 23 year old male was admitted for initiation of new medical treatment of his psychiatric condition. He is known to have WPW patern on his ECG without history of tachyarrhythmia. | |
|
II III
|
Characteristic: Other
findings: |
| Go
to WPW page Go to predominant R wave in V1 (R/S ratio >1). Go to axis deviation. | Go
to pseudo (infarction) Q wave. Go to main menu |