 |
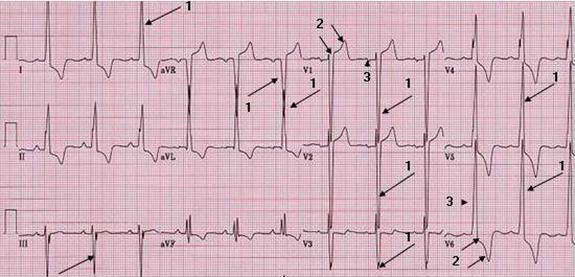
| HOCM. (Case 1) Pattern of LVH |
| HOCM (Hypertrophic Obstructive CardioMyopathy) usually has LVH pattern. |
| 1 = leads commonly used for voltage criteria. 2 = T wave inversion with ST depression (example in V6), T wave upright with ST elevation (example in V1). 3 = intrinsicoid deflection (time from begin of QRS to peak domminant R or S wave) in V6, and P wave in V1. |
| Patient. 84 year old female known having HOCM. She was admitted for chest pain required recurrent admissions and has been denied interventional treatment. This admission she has diagnosis of non Q wave MI and agreed to have stent placement to LAD. She also has history of hypertension. All of her ECGs look similar. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Go
to Giant T wave inversion menu
Go
to LVH menu / Go
to HOCM menu / Go
to specific diagnosis / Go
to main menu